Best Cosmetic & Plastic Surgeons in Indraprastha Apollo Hospital Delhi
 29 January,2026
Read More
29 January,2026
Read More
Enquire now in case of any assistance needed
 02 December,2024
02 December,2024
Cancer is a word that terrifies everyone. But is it really that scary? Well, the answer is both yes and no. When detected early, cancer can be beaten with medications and surgery. However, in the late stages, it becomes difficult to cure cancer, and the treatment revolves around palliative care and improving the patient's quality of life. This goes for all cancers, including skin cancer.
According to the IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer), over 1.5 million new cases of skin cancer were detected globally in 2022. With skin cancer cases growing at an alarming rate, it is important to raise awareness of the importance of early detection. In this blog, we will learn all about skin cancer, including its types, signs, treatment options, and prevention.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Have you ever wondered why doctors emphasize sunscreen and limit sun exposure? Skin cancer is a disease condition in which skin cells grow uncontrollably due to damage, usually caused by the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays. Skin cells grow old and die naturally but are replaced by new cells. When this normal functioning is hampered, they can grow more quickly and form a cluster that can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Skin cancer has become one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide. While it often develops on body parts exposed to the sun—like the face, arms, and legs—it can appear anywhere, even on areas rarely exposed, like the soles of your feet or under your nails. Skin cancer can affect anyone, but early detection and proper care can make a difference.
Did you know there are multiple types of skin cancer, each with different warning signs and levels of severity? Here are the main ones:
All types of skin cancer share a common factor: abnormal cell growth triggered by DNA damage. Regardless of the type, skin cancer can cause permanent damage if left untreated. In advanced stages, it may spread to other parts of the body. The good news? Early detection saves lives. Regular skin checks and awareness of changes are your best defenses.
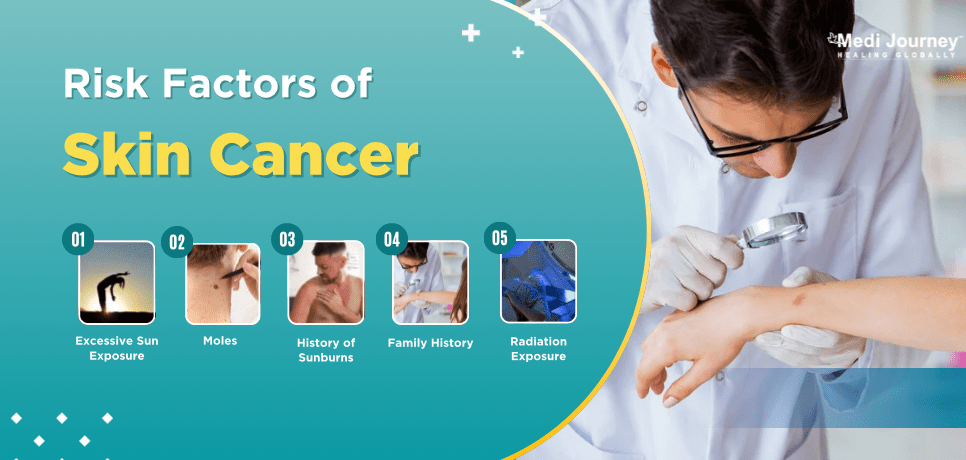
Have you ever wondered why some people get skin cancer while others don't? It is because there are a number of risks and causes of the disease. The foremost cause of skin cancer is exposure to UV light from tanning beds or directly from the sun. The radiation damages the DNA in your skin cells, leading to uncontrolled growth.
Certain factors increase your risk:
Does any of this sound familiar? If so, taking extra precautions is essential.
Have you ever noticed a spot on your skin that didn't seem right? Early skin cancer can be subtle and easy to overlook. You must know the signs to watch out for to detect skin cancer early. Look for:
Skin cancer looks different based on the type of cancer. To recognize warning signs, use the ABCDE rule:
If something doesn't look or feel normal, it's time to visit a dermatologist.
The common signs and symptoms associated with skin cancer are:
What happens during a skin cancer check? A dermatologist might ask you if you have noticed any changes in your existing moles, freckles, or other skin spots or if you have seen any new growths on your skin. They will examine your skin carefully and may use a special tool to look at suspicious spots. If they suspect cancer, they'll perform a biopsy, taking a small sample of the affected skin. This sample is then tested in a lab to confirm whether it's cancer and determine its type.
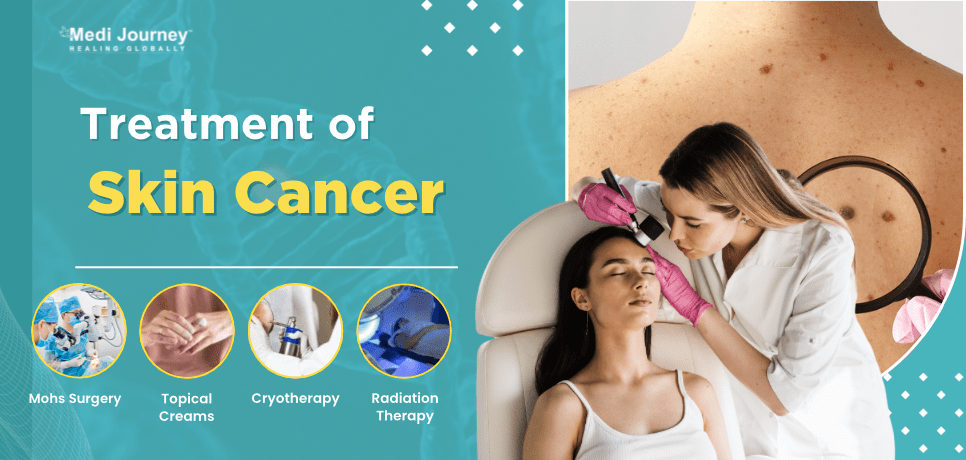
What happens if you're diagnosed with skin cancer? Treatment depends on the type and stage of the cancer, but here's what you might expect:
Isn't it amazing to know that you can remarkably reduce your risk of developing skin cancer with a few simple steps? Here's how to protect your skin and avoid skin cancer:
Preventing skin cancer is easier than treating it, so why not start today?
Did you know doctors can treat some types of skin cancer without surgery? Prescription creams containing chemo drugs like 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) are often used for early-stage cancers. Imiquimod is a type of immunotherapy that you can apply topically. These creams work by boosting your immune system or directly killing abnormal cells.
Diclofenac is an NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) that can be applied as a 3% gel. It is prescribed for superficial or low-risk BCCs. Ingenol mebutate gel is also indicated for the treatment of low-risk BCCs. It Induces cell death and local immune response.
However, these creams aren't suitable for every type of cancer, so always consult a dermatologist before starting treatment.
Here's something to think about: older men with fair skin, especially those over 50, are most at risk of dying from skin cancer. Why? They often spend years exposed to the sun and may delay seeking treatment for suspicious spots. Early detection is crucial—no matter your age or gender.
The cost of skin cancer treatment in India ranges between USD 3,000 and USD 6,000. It is 50-70% lower than in developed nations such as the USA and the UK. Below are the average prices of various treatments available for skin cancer:
Skin cancer may look like a mole or a spot on your skin. Knowing the risk factors and recognizing the symptoms can help you catch them early. If detected early, skin cancer can be treated and often cured. So, how will you protect your skin today? Remember, being aware can help keep you safe and healthy.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Doctor of Pharmacy
Dr. Deepanshu Siwach is a skilled clinical pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree.?He has 4+?years of experience and has worked with thousands of patients. He has been associated with some of the top hospitals, such as Artemis Gurgaon.
Dr. Monica Bambroo is an experienced Dermatologist and Dermato-Surgeon. She is an expert filler injector and has experience in both basic and advanced indications. Dr. Bambroo has conducted numerous non-invasive skin tightening procedures....
Senior Consultant
Medical Oncologist
Nanavati Super Specialty Hospital, Mumbai
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsThe Art of Effective Communication
 27 January,2026
Read More
27 January,2026
Read More
 20 January,2026
Read More
20 January,2026
Read More
 16 January,2026
Read More
16 January,2026
Read More
 13 January,2026
Read More
13 January,2026
Read More
 09 January,2026
Read More
09 January,2026
Read More
Trusted by Patients
"I am Asim from Bangladesh and was looking for treatment in India for neuro. I visited many websites to get the complete information regarding the treatment but I was not satisfied as I was getting confused. In the meanwhile, one of my friends suggested I seek help from Medi Journey as he experienced his medical journey very smoothly and was satisfied with it. They have filtered the top 10 doctors as per experience, the success rate of surgery & profile, so it helps us to choose the best treatment in India. "
"For my knee surgery, Medi Journey guided me to BLK Hospital where I received exceptional care. The team's support and the expertise at BLK Hospital exceeded my expectations. Thank you Medi Journey for making my medical journey stress-free. "
"I came from Iraq for my granddaughter's eye surgery in India facilitated by Medi Journey, due to critical cases they advised us to get a second opinion from the different hospitals before going to surgery. Finally, we went to Fortis Escort Hospital, which helped us to get more confidence for diagnosis. Fortis Escort Hospital has the best eye surgeon team with the latest instruments. Thanks to all team members for providing a high-quality treatment in India at an affordable cost. "
"I came for my hair transplant in India, before coming I was so confused about choosing the best clinic and surgeon for me. But thanks to God one of my friends had a hair transplant in India through Medi Journey. He recommended me to go with them. I am completely happy with my experience with them. They were always very fast in their responses to me. the success rate of my hair transplant surgery is 100%."
"Artemis Hospital, suggested by Medi Journey, turned out to be a great choice for my treatment. The personalized assistance and medical care were exceptional. I'm grateful to Medi Journey for guiding me to a hospital that perfectly matched my needs. Highly recommended! "
"I came from Afghanistan for my treatment in India at Jaypee Hospital, Noida. I had a fantastic experience with Medi Journey. Kudos to them for their incredible support during my medical journey. They not only took care of all the logistics but also connected me with a fantastic healthcare team. Efficient, caring, and highly recommended for a hassle-free medical tourism experience."
"I am Adam from Kano, Nigeria, one of my friends from Nigeria was facilitated by Medi Journey, and he recommended us to go with them. I sent my all reports to them and within 48 hours they reverted with 4 options from different hospitals. They helped me to get a Visa letter from the hospital, arrange pick-up from the airport, and book a hotel for me. Their team is very honest and throughout our stay in India they are with us they are caring for us like his family members. BLK Hospital is the best hospital in India with a top surgical oncologist surgeon team, a very advanced OT, and a Radiotherapy department. I wish more success to Medi Journey. "
"Great experience at the Max Hospital for my spine surgery and was successfully done. I thank my neurosurgeon and his entire team. I recommended all of my country's people to Medi Journey for treatment in India, they choose the best hospital, the best doctors, and the best cost for patients."
"I came to India from Dhaka, Bangladesh for my father-in-law's cardiac surgery at Fortis Hospital. I was confused about choosing the best surgeon for him before coming, but their team helped me to choose the best hospital and best cardiac surgeon in India with very good cost and 100% success rate of surgery. I am very happy with the services, really they make my journey so comfortable that make me feel at home. Thanks again and I like people to choose "Medi Journey" as your travel guide. "
"I am Mohammad from Bangladesh came to India for my general health checkup. Medi Journey offers me the complete package including Pick-up from the airport, hotel services, and 24-hour assistance. They guide you to choose the best hospital in India, the best cost of treatment with top-most doctors and give you complete information about hotel booking, and pick-up from the airport before coming to India They have the best team to help. Always choose Medi Journey for your treatment in India."





