Best Cosmetic & Plastic Surgeons in Indraprastha Apollo Hospital Delhi
 29 January,2026
Read More
29 January,2026
Read More
Enquire now in case of any assistance needed
 19 June,2025
19 June,2025
Recovering from back surgery is a journey that requires patience, dedication, and the right approach to pain management. While medications can provide temporary relief, relying solely on them may lead to dependency, side effects, and incomplete healing. Instead, adopting effective pain management strategies after back surgery can empower you to take control of your recovery, naturally reduce discomfort, and improve long-term outcomes.
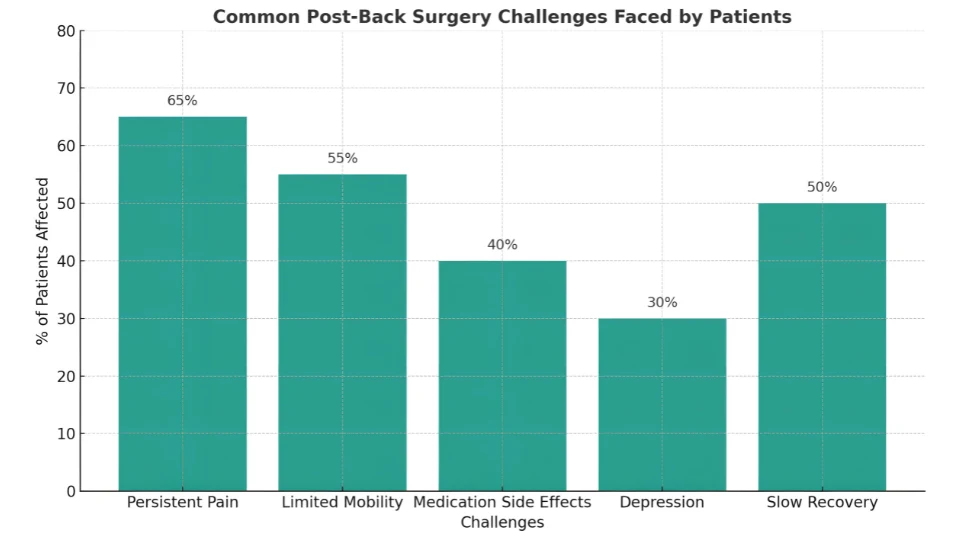 This graph highlights the most common post-op challenges, underscoring the need for holistic, non-drug pain management strategies to support a smoother, more sustainable recovery.
This graph highlights the most common post-op challenges, underscoring the need for holistic, non-drug pain management strategies to support a smoother, more sustainable recovery.
This guide is designed to offer real value by exploring proven, drug-free, effective pain management strategies that promote healing, restore mobility, and enhance overall well-being. Whether you’re a recent post-op patient or a caregiver seeking the best recovery plan, these strategies will help you achieve a pain-free, active life without over-relying on pharmaceuticals.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Back surgery, whether it’s a discectomy, fusion, or laminectomy, is a significant medical intervention. While it can correct structural issues, the post-operative phase is critical for ensuring long-term success. Unfortunately, many patients struggle with:
By focusing on effective pain management strategies after back surgery, you can:
Let’s explore the most valuable, evidence-based strategies to optimize your recovery.
One of the most effective pain management strategies is a customized physical therapy (PT) plan. A skilled therapist will guide you through exercises that:
Key PT Techniques for Back Surgery Recovery
Neurostimulation / Neuro-modulation
Pro Tip: Start physical therapy (PT) as soon as your surgeon approves; delaying can lead to stiffness and a slower recovery.
A highly effective pain management strategy after back surgery (beyond medication) is alternating between cold and heat therapy.
When to Use Cold Therapy (Ice Packs)
When to Use Heat Therapy (Heating Pads/Warm Baths)
Safety Note: Always wrap ice/heating sources in a cloth to prevent skin damage.
Pain is not solely physical; it is intricately linked to stress and emotions. Utilizing mind-body techniques is a highly effective strategy for managing pain following back surgery.
Deep Breathing & Meditation
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
Biofeedback Therapy
Value Insight: Studies show that patients who practice mindfulness report 30% less pain intensity post-surgery.
Acupuncture: Fine needles stimulate nerves to block pain signals.
Acupressure: Applying finger pressure on key points (e.g., LI4 for pain relief).
Benefits of Acupuncture Post-Surgery
Important: Seek a licensed acupuncturist with experience in post-surgical care.
For some patients, gentle spinal adjustments can help:
Warning: Always get a surgeon's approval before seeing a chiropractor, especially after spinal fusion.
A licensed massage therapist can use post-surgical techniques to:
Best types:
What you eat directly impacts healing. When it comes to effective pain management strategies, adhere to these dietary guidelines:
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Protein-Rich Foods for Tissue Repair
Hydration & Supplements
Avoid: Sugar, processed foods, and excessive caffeine (they increase inflammation).
Poor sleep worsens pain. Improve rest with:
Overexertion can cause setbacks. Follow these rules:
Chronic pain can lead to anxiety/depression. Seek:
By embracing these effective pain management strategies after back surgery, you’re not just masking pain; you’re actively healing. From physical therapy and mind-body techniques to proper nutrition and gradual activity, these drug-free approaches promote lasting recovery.
Remember, healing takes time. Stay consistent, work with your healthcare team, and trust the process. Your commitment to these Pain Management Strategies After Back Surgery (Beyond Medication) will help you build a stronger, more resilient back, naturally and sustainably. If you want to know more about pain management strategies, contact us today. MediJourney can help you manage chronic pain in a sustainable way that lasts a lifetime.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
B.Sc in Media Science from NSHM Knowledge Campus, Kolkata, 2019-2022
Suryani Dutta is an experienced content writer, specializing in healthcare and medical tourism. With a B.Sc. in Media Science from NSHM Knowledge Campus, Kolkata, she creates engaging, accurate, and SEO-friendly content that empowers patients to make info
A renowned Neuro-spine Surgeon, Dr. S K Rajan, has successfully performed over 3000 surgeries, including intricate spine cases. With over 25 years of experience, his expertise lies in minimally invasive (keyhole) spine surgery, Craniovertebral junction (...
Senior Consultant
Medical Oncologist
Nanavati Super Specialty Hospital, Mumbai
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsThe Art of Effective Communication
 27 January,2026
Read More
27 January,2026
Read More
 20 January,2026
Read More
20 January,2026
Read More
 16 January,2026
Read More
16 January,2026
Read More
 13 January,2026
Read More
13 January,2026
Read More
 09 January,2026
Read More
09 January,2026
Read More
Trusted by Patients
"I am Asim from Bangladesh and was looking for treatment in India for neuro. I visited many websites to get the complete information regarding the treatment but I was not satisfied as I was getting confused. In the meanwhile, one of my friends suggested I seek help from Medi Journey as he experienced his medical journey very smoothly and was satisfied with it. They have filtered the top 10 doctors as per experience, the success rate of surgery & profile, so it helps us to choose the best treatment in India. "
"For my knee surgery, Medi Journey guided me to BLK Hospital where I received exceptional care. The team's support and the expertise at BLK Hospital exceeded my expectations. Thank you Medi Journey for making my medical journey stress-free. "
"I came from Iraq for my granddaughter's eye surgery in India facilitated by Medi Journey, due to critical cases they advised us to get a second opinion from the different hospitals before going to surgery. Finally, we went to Fortis Escort Hospital, which helped us to get more confidence for diagnosis. Fortis Escort Hospital has the best eye surgeon team with the latest instruments. Thanks to all team members for providing a high-quality treatment in India at an affordable cost. "
"I came for my hair transplant in India, before coming I was so confused about choosing the best clinic and surgeon for me. But thanks to God one of my friends had a hair transplant in India through Medi Journey. He recommended me to go with them. I am completely happy with my experience with them. They were always very fast in their responses to me. the success rate of my hair transplant surgery is 100%."
"Artemis Hospital, suggested by Medi Journey, turned out to be a great choice for my treatment. The personalized assistance and medical care were exceptional. I'm grateful to Medi Journey for guiding me to a hospital that perfectly matched my needs. Highly recommended! "
"I came from Afghanistan for my treatment in India at Jaypee Hospital, Noida. I had a fantastic experience with Medi Journey. Kudos to them for their incredible support during my medical journey. They not only took care of all the logistics but also connected me with a fantastic healthcare team. Efficient, caring, and highly recommended for a hassle-free medical tourism experience."
"I am Adam from Kano, Nigeria, one of my friends from Nigeria was facilitated by Medi Journey, and he recommended us to go with them. I sent my all reports to them and within 48 hours they reverted with 4 options from different hospitals. They helped me to get a Visa letter from the hospital, arrange pick-up from the airport, and book a hotel for me. Their team is very honest and throughout our stay in India they are with us they are caring for us like his family members. BLK Hospital is the best hospital in India with a top surgical oncologist surgeon team, a very advanced OT, and a Radiotherapy department. I wish more success to Medi Journey. "
"Great experience at the Max Hospital for my spine surgery and was successfully done. I thank my neurosurgeon and his entire team. I recommended all of my country's people to Medi Journey for treatment in India, they choose the best hospital, the best doctors, and the best cost for patients."
"I came to India from Dhaka, Bangladesh for my father-in-law's cardiac surgery at Fortis Hospital. I was confused about choosing the best surgeon for him before coming, but their team helped me to choose the best hospital and best cardiac surgeon in India with very good cost and 100% success rate of surgery. I am very happy with the services, really they make my journey so comfortable that make me feel at home. Thanks again and I like people to choose "Medi Journey" as your travel guide. "
"I am Mohammad from Bangladesh came to India for my general health checkup. Medi Journey offers me the complete package including Pick-up from the airport, hotel services, and 24-hour assistance. They guide you to choose the best hospital in India, the best cost of treatment with top-most doctors and give you complete information about hotel booking, and pick-up from the airport before coming to India They have the best team to help. Always choose Medi Journey for your treatment in India."





