Top Nephrologists in Indraprastha Apollo Hospital Delhi
 04 February,2026
Read More
04 February,2026
Read More
Enquire now in case of any assistance needed
 20 May,2024
20 May,2024

Liver cancer is becoming increasingly common, with over 900,000 cases recorded worldwide each year. It is more prevalent in regions like Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. Late-stage liver cancer is difficult to treat and often results in death. Hence, early detection is crucial for successful treatment. If you or anyone you know has been diagnosed with liver cancer, making an informed decision quickly is essential to ensure better outcomes. This blog aims to provide detailed information regarding the various risk factors of liver cancer and the various prevention and treatment options available.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
The liver is a crucial body organ responsible for several vital functions, such as digestion, bile production, nutrient storage, blood filtering, medication metabolism, and more.
Liver cancer occurs when liver cells experience uncontrolled growth. If the cancer originates in the liver, it is called primary liver cancer. In contrast, if the cancer comes from another part of the body and spreads to the liver, it is called secondary liver cancer.
There are three primary types of liver cancer, which include:
HCC and IHC are more common in men than women, and people between the ages of 55 and 64 are most often diagnosed with these types of liver cancer. Furthermore, people whose race includes Asian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic, or American Indian/Alaskan Indian are more susceptible to developing primary liver cancer than those who are Black or white.
Liver cancer symptoms can be pretty vague, making it difficult to diagnose in the early stages. Therefore, awareness of the risk factors and what signs to look for is necessary.
Here are some of the signs and symptoms of liver cancer. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it does not necessarily mean that you have liver cancer. However, it is always advisable to consult the best oncologists and get regular health check-ups. The symptoms of liver cancer include:
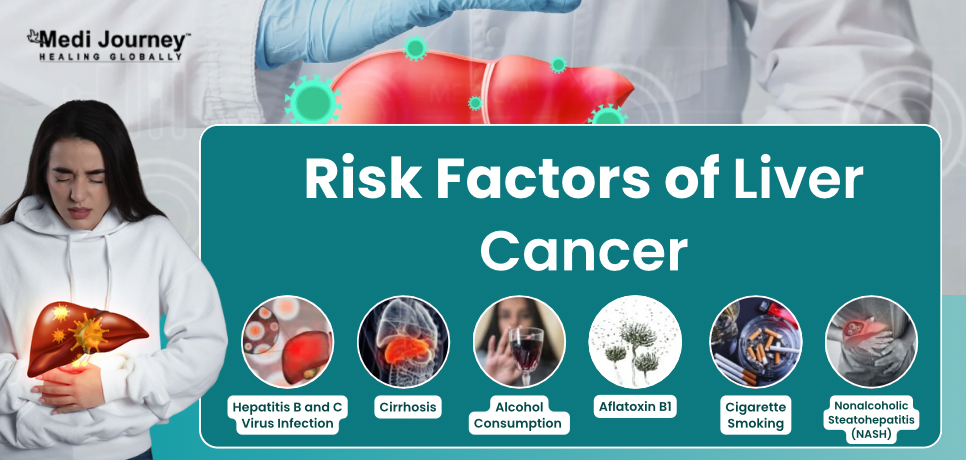
Liver cancer is identified as the third leading cause of cancer-associated deaths worldwide. While diseases can affect any individual, researchers have identified certain risk factors for them. These include –
Hepatocellular carcinoma or liver cancer can be diagnosed in several ways. If the doctor suspects liver cancer during a physical examination, they may further order diagnostic tests such as –
You cannot prevent liver cancer entirely. However, knowing the risk factors and following a few steps can reduce your chances of developing the disease. Preventive measures for liver cancer are –
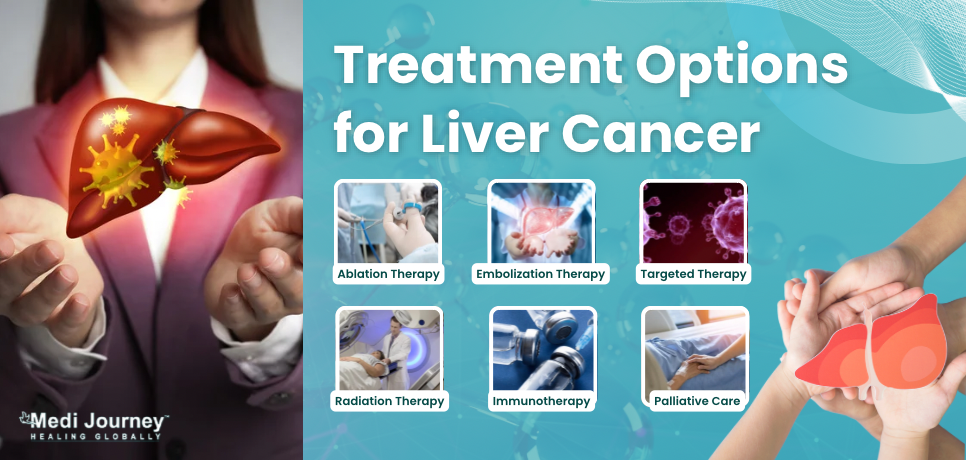
Treatment for liver cancer is decided based on stage and type of cancer. Oncologists can use a combination of treatment options for managing liver cancer. Following are the multiple treatment modalities available to treat primary liver cancer.
Surgery involves removing a tumor along with some healthy tissue surrounding it. It is a highly effective treatment for liver cancer, particularly for patients with good liver function and tumors that surgeons can safely remove from a limited part of the liver. However, patients may not be eligible for surgery if the cancer has spread outside of the liver, their liver is too damaged, or if they have other serious illnesses.
There are two types of surgery used to treat liver cancer:
Embolization therapy treats liver tumors by blocking or reducing the flow of blood through the hepatic artery to the tumor. This procedure restricts the oxygen and nutrients the cancer needs to survive, causing it to stop growing. The therapy is typically used for individuals who cannot undergo surgery or ablation therapy and whose tumors have not spread outside the liver.
Two main types of embolization therapy are transarterial embolization (TAE) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
Ablation therapy is a type of treatment that can remove or destroy tissue. In the case of liver cancer, different types of ablation therapies can be used. These include:
To make radiation more effective, radiation oncologists administer radiation therapy in a series of treatments that allow healthy cells to recover. The number of treatments they prescribe depends on the cancer's specific details, including the tumor's size and location. To prevent radiation from damaging nearby healthy tissue, healthcare professionals employ specific methods of giving external radiation therapy, including:
Immunotherapy is a biological cancer treatment that enhances the immune system's ability to disrupt cancer cells. It uses the body's natural defenses to fight against cancer.
Targeted therapy is an effective cancer treatment that specifically targets cancer cells and limits the damage to healthy cells. This type of treatment aims to block cancer cell's growth and spread.
Palliative care is a specialized form of oncology care focusing on alleviating pain and other symptoms associated with severe illnesses.
Liver cancer is a serious medical condition, but early detection and treatment can improve the probability of a successful outcome. You can take charge of your liver health by understanding the risk factors, taking preventive measures, and getting regular checkups. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with liver cancer, remember that there are many treatment options available. Working with a team of oncologists, you can make a treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Doctor of Pharmacy
Dr. Deepanshu Siwach is a skilled clinical pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree.?He has 4+?years of experience and has worked with thousands of patients. He has been associated with some of the top hospitals, such as Artemis Gurgaon.
Dr. Vivek Gupta is an experienced Surgical Oncologist with over 16 years of practice....
Senior Consultant
Medical Oncologist
Nanavati Super Specialty Hospital, Mumbai
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsThe Art of Effective Communication
 04 February,2026
Read More
04 February,2026
Read More
 02 February,2026
Read More
02 February,2026
Read More
 27 January,2026
Read More
27 January,2026
Read More
 20 January,2026
Read More
20 January,2026
Read More
 16 January,2026
Read More
16 January,2026
Read More
Trusted by Patients
"I am Asim from Bangladesh and was looking for treatment in India for neuro. I visited many websites to get the complete information regarding the treatment but I was not satisfied as I was getting confused. In the meanwhile, one of my friends suggested I seek help from Medi Journey as he experienced his medical journey very smoothly and was satisfied with it. They have filtered the top 10 doctors as per experience, the success rate of surgery & profile, so it helps us to choose the best treatment in India. "
"For my knee surgery, Medi Journey guided me to BLK Hospital where I received exceptional care. The team's support and the expertise at BLK Hospital exceeded my expectations. Thank you Medi Journey for making my medical journey stress-free. "
"I came from Iraq for my granddaughter's eye surgery in India facilitated by Medi Journey, due to critical cases they advised us to get a second opinion from the different hospitals before going to surgery. Finally, we went to Fortis Escort Hospital, which helped us to get more confidence for diagnosis. Fortis Escort Hospital has the best eye surgeon team with the latest instruments. Thanks to all team members for providing a high-quality treatment in India at an affordable cost. "
"I came for my hair transplant in India, before coming I was so confused about choosing the best clinic and surgeon for me. But thanks to God one of my friends had a hair transplant in India through Medi Journey. He recommended me to go with them. I am completely happy with my experience with them. They were always very fast in their responses to me. the success rate of my hair transplant surgery is 100%."
"Artemis Hospital, suggested by Medi Journey, turned out to be a great choice for my treatment. The personalized assistance and medical care were exceptional. I'm grateful to Medi Journey for guiding me to a hospital that perfectly matched my needs. Highly recommended! "
"I came from Afghanistan for my treatment in India at Jaypee Hospital, Noida. I had a fantastic experience with Medi Journey. Kudos to them for their incredible support during my medical journey. They not only took care of all the logistics but also connected me with a fantastic healthcare team. Efficient, caring, and highly recommended for a hassle-free medical tourism experience."
"I am Adam from Kano, Nigeria, one of my friends from Nigeria was facilitated by Medi Journey, and he recommended us to go with them. I sent my all reports to them and within 48 hours they reverted with 4 options from different hospitals. They helped me to get a Visa letter from the hospital, arrange pick-up from the airport, and book a hotel for me. Their team is very honest and throughout our stay in India they are with us they are caring for us like his family members. BLK Hospital is the best hospital in India with a top surgical oncologist surgeon team, a very advanced OT, and a Radiotherapy department. I wish more success to Medi Journey. "
"Great experience at the Max Hospital for my spine surgery and was successfully done. I thank my neurosurgeon and his entire team. I recommended all of my country's people to Medi Journey for treatment in India, they choose the best hospital, the best doctors, and the best cost for patients."
"I came to India from Dhaka, Bangladesh for my father-in-law's cardiac surgery at Fortis Hospital. I was confused about choosing the best surgeon for him before coming, but their team helped me to choose the best hospital and best cardiac surgeon in India with very good cost and 100% success rate of surgery. I am very happy with the services, really they make my journey so comfortable that make me feel at home. Thanks again and I like people to choose "Medi Journey" as your travel guide. "
"I am Mohammad from Bangladesh came to India for my general health checkup. Medi Journey offers me the complete package including Pick-up from the airport, hotel services, and 24-hour assistance. They guide you to choose the best hospital in India, the best cost of treatment with top-most doctors and give you complete information about hotel booking, and pick-up from the airport before coming to India They have the best team to help. Always choose Medi Journey for your treatment in India."





